
Synapsis, crossing over and recombination occurs.Īt the start of prophase I, the chromosomes have already duplicated. The pairing of homologous chromosomes takes place.It is the most complicated and longest phase of meiosis. Long phase divided into substages (Leptotene, zygotene.

Prophase I is the longest phase of meiosis, typically consuming 90% of the time for the two divisions. What is the difference between karyokinesis and cytokinesis 3. The nuclear envelope disappears at the end of prophase I, allowing the spindle to enter the nucleus. SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS ( Carrying 2 or 3 marks each ) 1.

The resulting structure, consisting of four chromatids, is called a tetrad. Homologous chromosomes each composed of 2 sister chromosomes come jointly as pairs.
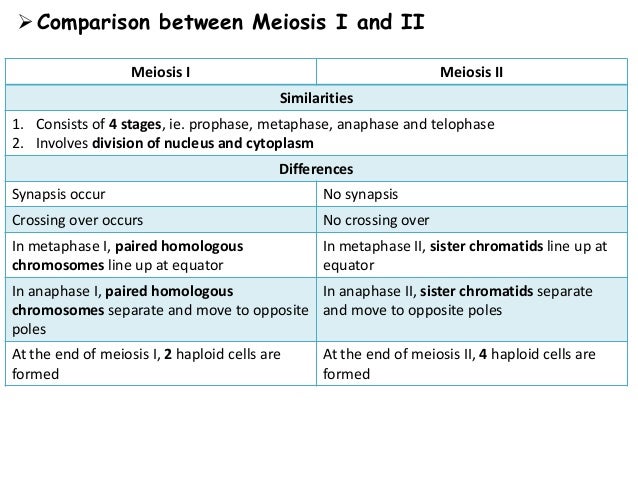
Part exchange does not occur in the chromosome.Mitosis occurs after interphase in eukaryotes. With a replicated genome and organelles, the cell can begin mitosis. This includes the centrosome, within which the centriole gets replicated. During interphase, the DNA is replicated, along with the organelles necessary to divide. Pair formation in between homologous chromosomes does not occur as there is no attraction between them.Each duplicated chromosome appears as 2 sister chromatids joined simultaneously. It is a short phase and is not divided into any subphase.The homologous chromosomes pair together in prophase 1 of meiosis, but they do not throughout prophase 1 of mitosis.ĭifference between Prophase of Mitosis and Prophase-1 of Meiosis Metaphase-1 of meioses are the pairs of chromosomes (bivalents) become arranged on the metaphase plate and are attached to the now fully formed meiotic spindle. Homologous chromosomes can exchange parts in a process called "crossing over.Metaphase is the third phase of mitosis, the process that separates duplicated genetic material carried in the nucleus of a parent cell into two identical daughter cells. In Metaphase I, homologous chromosome pairs line up. This shuffling process is known as recombination or "crossing over" and occurs while the chromome pairs are lined up in Metaphase I. Each sibling is 50% mom and 50% dad, but which 50% of each can vary in the siblings. But this happens independently for each trait, so just because you got your dad's brown eyes doesn't mean you'll get his blond hair too. Each sperm and egg will end up with either B or b from mom and either B or b from dad. This leads to four possibilities: You could get B from mom and B from dad, or B from mom and b from dad, or b from mom and B from dad, or b from mom and b from dad. Imagine, for example, that eye color was controlled by a single gene, and that mom could have B, the allele for brown eyes or b, the allele for blue eyes, and dad could also have B or b. But each non-identical-twin child of these parents ends up with a different combination. You ended up with half of mom's paired genes and half of dad's paired genes. Your parents each have at least one pair of alleles (versions of a gene) for every trait (and many pairs of alleles for each polygenic trait).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
